Tech
How MIT ended up on Memorial Drive
Published
2 years agoon
By
Drew Simpson
On March 23, 1912, the very day the subway connecting Boston and Cambridge opened to the public, another event took place that would change Kendall Square even more profoundly than the new, state-of-the-art transit system. As fate would have it, that was the day when a large swath of property adjacent to the square was formally conveyed to MIT, paving the way for the school’s move across the river from the Back Bay.
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology today forms such an essential part of Kendall Square—intertwined with the very definition of what the square is—that it may seem surprising to learn that the Institute’s arrival was by no means certain. In fact, if an enterprising businessman named Charles Davenport had realized his vision for the marshland on the banks of the Charles River, it’s very unlikely that the university would have come to Cambridge at all.
Davenport had started out as a woodworker’s apprentice, got into the coach-making business, and ultimately sold his pioneering railcar-making operation at 700 Main Street in 1855. But he remained extremely interested in what was going on around what was then called Dock Square, even as he traveled throughout the United States, took several trips to Europe, and made at least one sojourn to Cuba. During a visit to Havana in the 1850s, Davenport got the inspiration for developing the shoreline on both sides of the Charles River into a vast park. In Cuba’s capital, the former wheelwright “saw the small embankment on the bay there, where the people sat under the palms, enjoying the breezes.” That made him think of the Charles River and the salt marshes and mudflats that lined it on both sides. He envisioned “a boulevard along each river bank … two hundred feet in width,” and a stately residential district occupying much of the area where MIT now stands, to mirror that of Boston’s Back Bay.
Davenport already owned some of the marshland on the Cambridge side of the river. Upon returning to Boston, he began buying up more. He eventually accumulated three-fourths of the shoreline flats between the Cottage Farm and West Boston bridges (now the Boston University and Longfellow bridges, respectively), a roughly 2.5-mile stretch on the Cambridge side of the river. It was, essentially, the backyard of both his own former carriage works and Edward Kendall’s boiler-making operation.
The section of the Charles River around what is now Kendall Square had long been unappealing. In the 1800s, the Charles was dammed upriver for mills, and the bordering marshlands were filled for commercial and residential developments. At low tide, the lower Charles, including the area near Kendall Square, became a settling ground for sewage. By the mid-1800s, several plans had been advanced to fill the mudflats and marshes and make the Charles into a world-class public space and park system, but there had been little traction by the time Davenport got active—and he meant to change that.
Davenport formed the Charles River Embankment Company with some associates in 1880 to pursue his dream of creating Havana-like esplanades on both sides of the river. In Cambridge, his plans included a seawall or embankment that would protect the wide public esplanade and the line of grand homes to be constructed just inland. All this was imagined for just upriver from Dock Square, almost exactly where MIT now sits.
Davenport envisioned “a boulevard along each river bank … two hundred feet in width,” and a stately residential district occupying much of the area where MIT now stands, to mirror that of Boston’s Back Bay.
It almost happened—and there would almost certainly have been no MIT in Cambridge if it had. In 1882, the cities of Cambridge and Boston agreed to build a new bridge across the widest part of the river basin (this became the Harvard Bridge, along what was later named Massachusetts Avenue). The Embankment Company negotiated a deal. By giving up the land the city needed for an approach to the bridge and for a 200-foot-wide esplanade, it received a postponement of any tax increases on the rest of its land during construction—and permission to develop it. This arrangement, says Cambridge historian Charles Sullivan, gave the company “the right to build a seawall, construct what’s now Memorial Drive, and fill all the land where MIT is now.”
Construction of the seawall began in 1883, and the Harvard Bridge was completed in 1892. The Embankment Company hired architect Frederick Viaux to draw up plans for an upscale residential neighborhood behind the esplanade, extending all the way back to the railroad track embankment that Davenport himself had helped build in the 1850s. Developers would have to abide by certain restrictions—including a 20-foot setback from the esplanade, a prohibition against industrial or commercial structures, a requirement to use only brick, iron, or stone as building materials, and a minimum height of three stories and maximum height of eight.
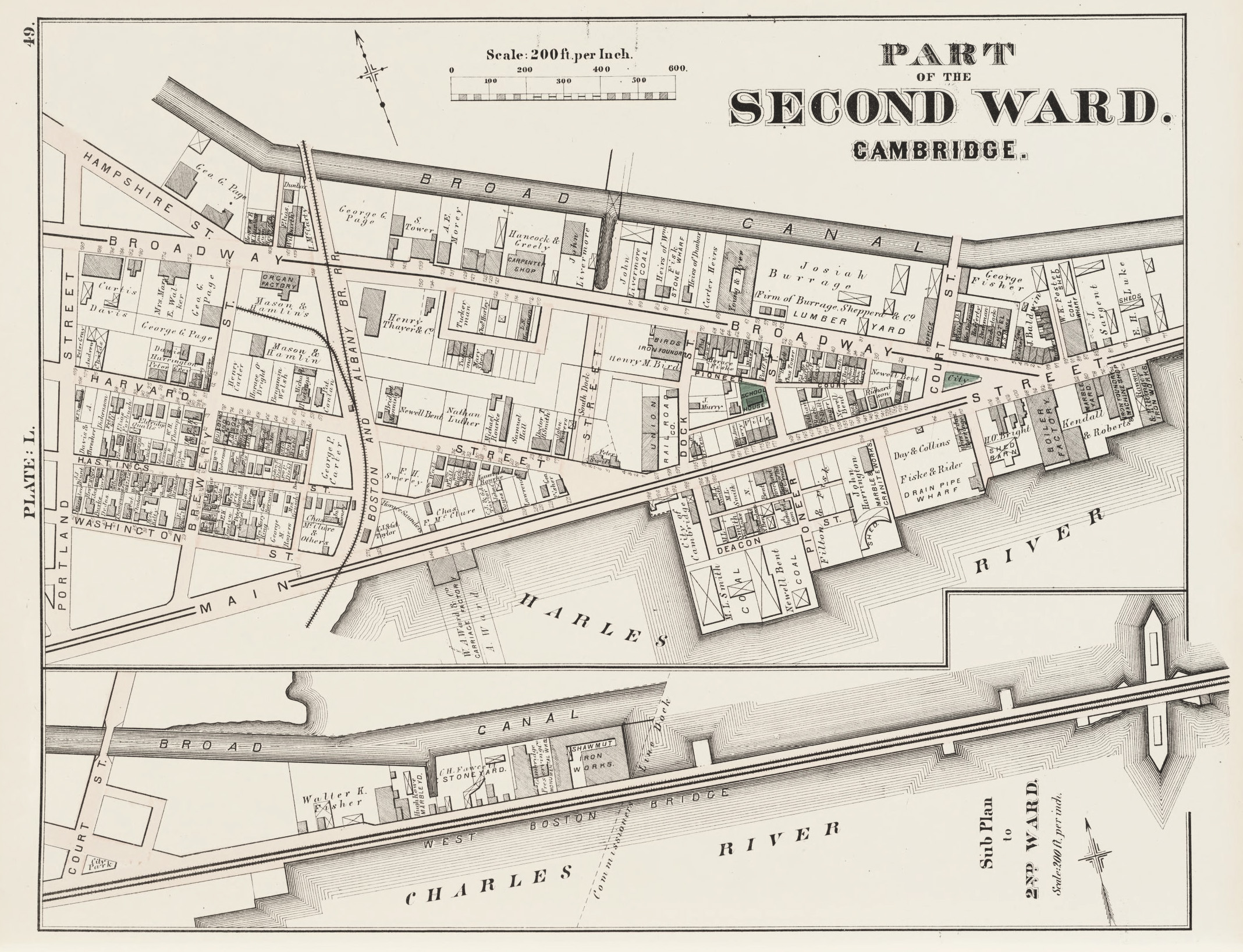
It all seemed compelling, but things started going haywire. More than 80% of the railroad tracks crossing Cambridge had been laid on a high embankment to protect the rails from the marshland below. The embankment had few culverts, severely cutting water flow from one side of the embankment to the other. That helped dry out the marshes north of the embankment and made them more suitable for development. But the river side of the rail line was still wet—and the marshlands reeked. By the late 1880s, an aging Davenport had essentially retired from business life. The Embankment Company he had helped form continued but found it hard to sell residential lots on that side, as the presence of the tracks discouraged many buyers.
Then came the devastating panic of 1893. The ensuing depression lasted until 1897 and forced the Embankment Company into bankruptcy. By then, a thousand feet of seawall had been constructed, and essentially all of the marshes and tide flats had been filled—creating solid land from Harvard Square all the way to East Cambridge. But little development took place for several years after the depression. By 1902, only the Riverbank Court Hotel at 305 Memorial Drive (now the MIT dorm Fariborz Maseeh Hall), the Metropolitan Storage Warehouse, the city armory (now MIT’s du Pont Athletic Center), and a smattering of other buildings had been completed. The lots Davenport’s group had envisioned for residential development sat unsold for the next 20 years, despite the expansive river and city views so appealing and sought after today.

The failure of Davenport’s plan opened the door for the arrival of MIT. But it took an unlikely series of events to bring the already famous school to Cambridge in 1916. A few years earlier, in fact, the odds were great that MIT itself would not long exist as an independent entity: the plan had been for it to merge with Harvard as the foundation of a new science and engineering campus across the Charles River in Brighton, about where Harvard Business School is today. Powerful figures, including steel baron Andrew Carnegie, had stakes in making the union a reality.
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology had been chartered as a land-grant school in 1861. By the late 1800s, what many knew as Boston Tech had proved its worth as a top-flight engineering and applied science school, arguably the country’s best. Its popularity strained the limits of its tight quarters in Boston’s Back Bay. By the early 1900s, MIT was scouting for a new home.
Harvard’s president, Charles Eliot, wanted that home to be Harvard. One of MIT’s inaugural chemistry professors, Eliot had become Harvard’s president in 1869. The Lawrence Scientific School, home to Harvard’s engineering and applied science program, was overshadowed by the college’s liberal arts reputation and struggled to attract enough students to justify its existence. So Eliot proposed to four successive presidents of Boston Tech that it and Harvard join forces. The fourth, Henry Pritchett, took the bait in the 1890s.
In January 1904, the Boston Daily Advertiser announced that Boston Tech and Harvard had agreed to merge. The surprise announcement set off a firestorm at MIT. While the agreement specified that the Institute would retain its name, charter, organization, and mission, the reality was that MIT would lose its cherished independence and become Harvard’s engineering school. That didn’t sit well with faculty, staff, or many alums. As one account summed up the concerns: “Should the Institute now, after nearly forty years’ struggle, give up its hard-won independence, sacrifice its fundamental principles, and yield a leadership won the hard way to come under the partial or complete domination of Harvard in the hope of monetary advantage?”
The answer from MIT faculty—by a vote of 56 to 7—was an overwhelming no. A survey sent to alumni showed 2,035 opposed and only 834 in favor. Nevertheless, in June 1905, the Technology Corporation gave the merger the green light by a vote of 23 to 15.
The union thus seemed ordained. In anticipation of the decision, a group of wealthy Harvard donors, including Andrew Carnegie and stockbroker Henry Higginson, had already pooled their resources and purchased the tract of riverfront property east of Soldiers Field in Brighton.
But there was one big catch. Under the terms of the agreement, MIT would be on the hook to “erect, furnish, and equip buildings having the capacity of at least its present buildings.” The school intended to sell all or part of its existing land in the Back Bay to fulfill this obligation. But in September 1905, only a few months after the Technology Corporation approved the plan, the Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court ruled that since MIT had purchased its land with federal land-grant funding, it did not have the right to sell it. The union with Harvard fell through. Pritchett, who resigned as MIT president in 1907, is perhaps best known for the deal’s failure even today.
MIT resumed its search for a new campus. The university had already considered the Cambridge esplanade site that Charles Davenport had tried to develop and rejected it. But it was put back on the table under the new president who arrived in 1909—the Scottish-born, New Zealand–raised mathematician and lawyer Richard Maclaurin. Maclaurin “saw clearly that his first and most urgent task would be the relocation of MIT and the raising of funds to build the ‘New Technology,’” the name given to the envisioned new campus. (The existing one was known simply as Technology.)
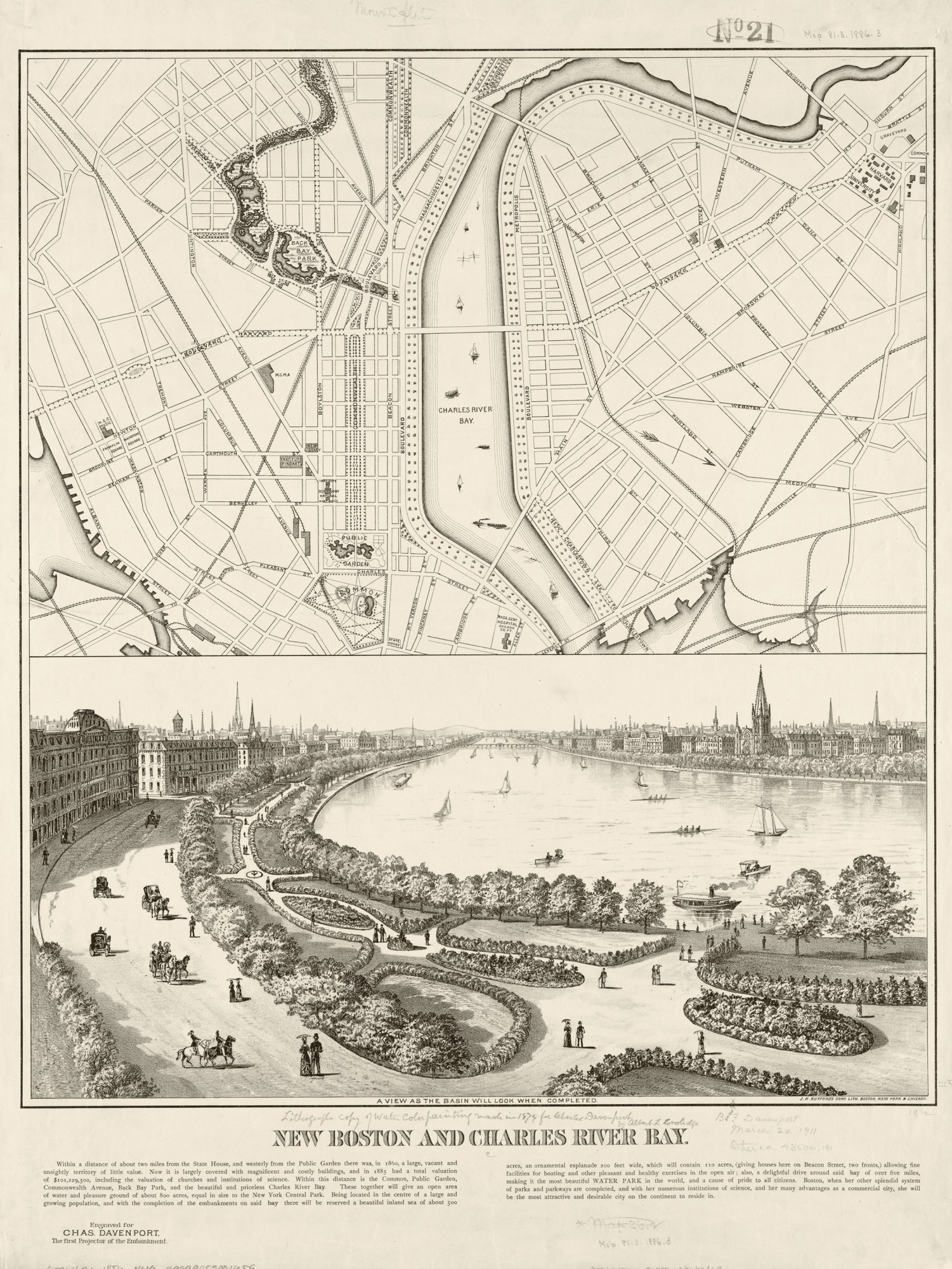
Maclaurin’s eyes were on the Cambridge esplanade even before he officially started. On a visit to Boston in April 1909, a few months before he took office, the Scotsman dined at the Beacon Street home of Charles Stone, a founder of the then 20-year-old engineering firm Stone & Webster (both Stone and cofounder Edwin Webster were MIT grads). They looked out the windows over the Charles to the esplanade property. The incoming president was enamored. According to one MIT history, “This struck Maclaurin as ideal for size, accessibility, and dignity of setting. A great and noble edifice could here be erected that would be a worthy home for the Institute.” Stone told Maclaurin it had already been ruled out, explaining that Cambridge would likely oppose another tax-exempt university inside its borders, that Harvard would probably object, and that several would-be donors—he must have been thinking of Higginson, Carnegie, and their partners—were unlikely to give generously to support a move to that site after the failed merger.



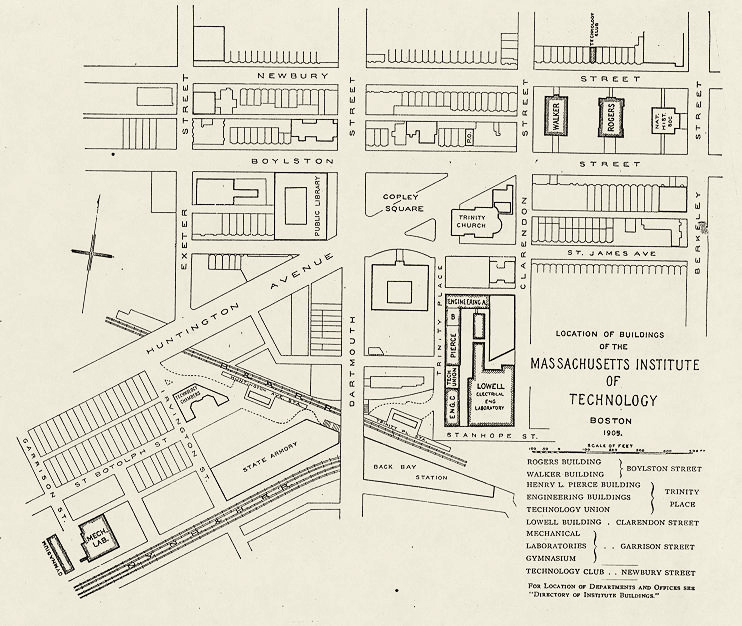
Maclaurin was not dissuaded. A formal new hunt for an expansion site launched with four main criteria: accessibility for students, faculty, and the public; affordability; space, with the potential for constructing buildings “worthy of the institute’s importance”; and a location “independent of the influence of other institutions.” The selection committee’s report, submitted to Maclaurin in October 1910, noted that the committee had considered at least 24 sites, even evaluating the possibility of building an island for the campus in the middle of the Charles, where the Harvard Bridge crossed it (this was soon deemed impractical). The most promising was a long stretch in Boston’s Fenway/Longwood area near the current Harvard Medical School campus and Simmons College. The esplanade site, called the Riverbank in the study, was a distant second, with a laundry list of potential problems. The report pointed out that the land was relatively costly and had a lot of owners—35, as it turned out—with whom to negotiate. The “encroaching manufacturing district” was deemed worrisome, as was the nearness to Harvard and that school’s potential objection to the move. Finally came the concerns about losing the school’s tax-exempt status.
In December, when Maclaurin tested the waters for a donation for any new site from Andrew Carnegie, “as Scotsman to Scotsman,” Carnegie turned him down flat: “Ye’re no blate. Just think of it, I hav given $3,800,000 towards extending the Pittsburg school … and you ask me to help Boston, which has received $400,000 from me for the Franklin Institute! I enjoy the joke! Besides, I do not put the Pittsburg school behind even the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It is a close race and we’ll see who is winner by and by.” Carnegie even pushed again for the merger with Harvard in a blunt P.S.: “If I mistake not, I am a part owner of that ground that my friend Lee Higginson and some of us purchased to unite the two institutions, which should be done.”
Maclaurin did get a pledge of $500,000 from T. Coleman du Pont, an MIT graduate and future US senator who was then president of his family’s namesake chemical business. But it was for a different site, a golf course in Allston. So perhaps in an effort to stir the pot, Maclaurin casually remarked to a newspaper reporter that “Technology might have to pull up stakes and move to someplace where the cost of living is within its means.”
Several Massachusetts cities quickly expressed their interest. A group of MIT alumni from Springfield offered land there, for example. Cities in other states weighed in as well. The Chicago Evening Post boasted: “We could support a ‘Boston Tech’ with our loose change, and we wouldn’t, like some cities we know of, have to search all the hinterland roundabout to find the money.”
The competition stirred officials in Cambridge to take action. “Restive at being rated as the only city in the state which Technology would never, never consider,” as Maclaurin’s biographer wrote, it dropped any objection to MIT’s retaining its tax-exempt status. The Cambridge City Council passed a formal resolution supporting the relocation, which was forwarded to Maclaurin by the mayor with his personal endorsement. In March 1911, Harvard notified Maclaurin it was now also okay with having both institutions in Cambridge.
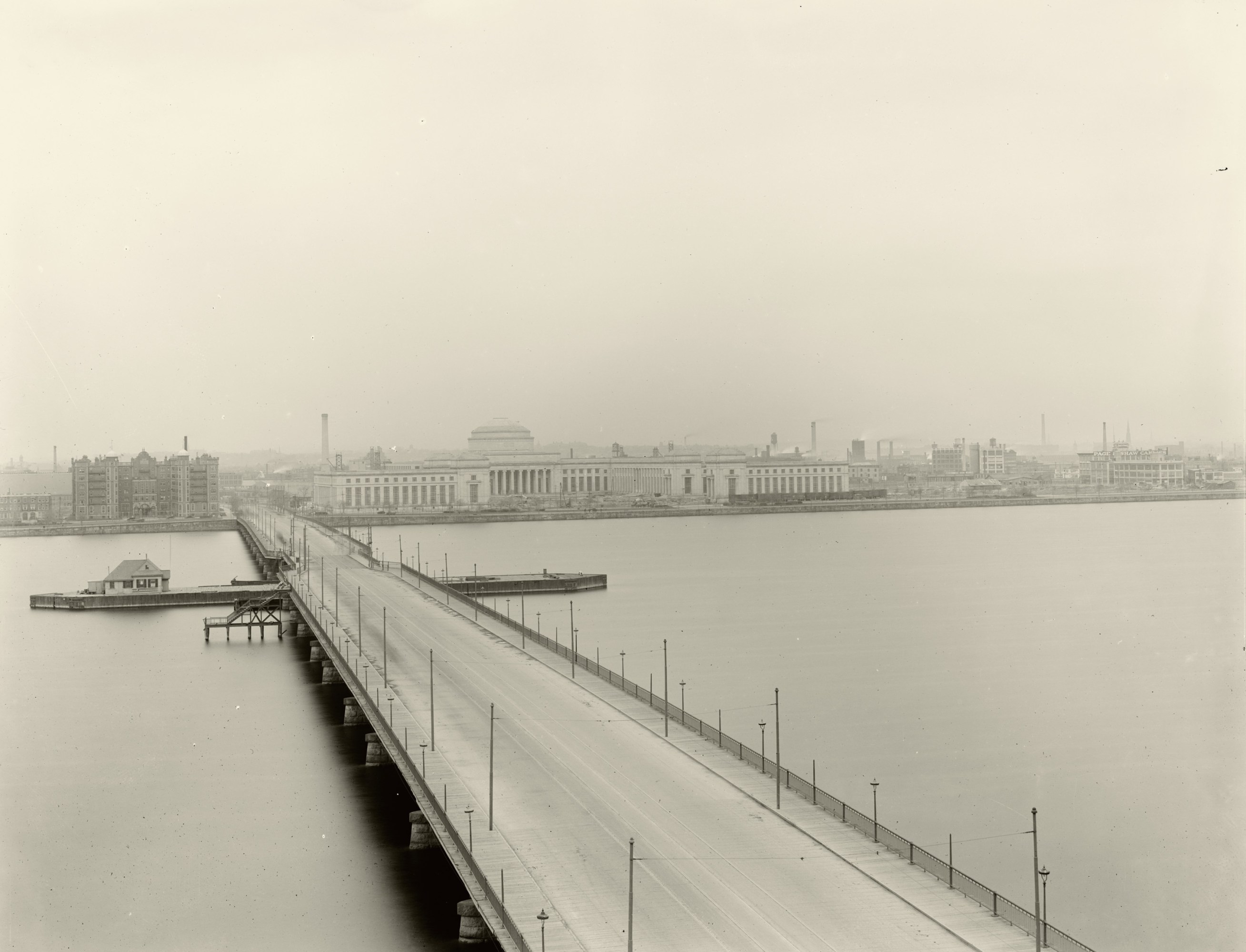
All this helped vault the Riverbank property to the top of the list—and loosen purse strings. Du Pont amended his pledge to extend it to the Cambridge property, and the state legislature approved a bill authorizing a grant of $100,000 a year to MIT for 10 years if the school raised a similar amount itself. By the fall of 1911, negotiations had been completed with all 35 owners of the Riverbank area to buy 46 acres of land bounded by Massachusetts Avenue on the west and Ames Street on the east, Vassar Street inland or north, and the esplanade. The envisioned campus did not extend east past Ames Street toward Main Street, where the MIT Media Lab and the MIT Sloan School of Management, among other buildings, stand today. Similarly, the land southwest of Massachusetts Avenue—now home to Kresge Auditorium, many student dorms (including the converted Riverbank Court Hotel), and the athletic center—was not part of the initial purchase. The price tag for the 46 acres was $775,000.
Then, in early 1912, Maclaurin met with Eastman Kodak founder George Eastman (who was neither an MIT alum nor a Massachusetts resident) at the Hotel Belmont in New York. They reportedly had a warm and earnest conversation, in which the MIT president detailed the plans for New Technology. As Maclaurin’s wife, Alice, later related, “The ground was broken so completely in Mr. Eastman’s mind that my husband was astonished. When Mr. Eastman was about to leave, he suddenly asked: ‘What will it cost to put up the new buildings?’ My husband answered that it would cost about two and a half million dollars. Mr. Eastman said, ‘I’ll send you a draft.’” Eastman’s one stipulation was that he remain anonymous—and so he was referred to only as Mr. Smith until his identity was revealed in 1920.
Although conveyance of the property to MIT took place on March 23, 1912, the same day the subway line officially debuted, it would take another four years for the first wave of construction and other elements to come together to enable MIT’s move. But a new era was visible on the horizon.

Where Futures Converge
Robert Buderi was editor at large and then editor in chief of Technology Review between 2000 and 2004. Excerpted from Where Futures Converge: Kendall Square and the Making of a Global Innovation Hub. Reprinted with permission from The MIT Press. Copyright 2022.
You may like
-


Emtech MIT is happening right now
-


Coming soon: MIT Technology Review’s 15 Climate Tech Companies to Watch
-

The Power of In-App Marketing Campaigns: Re-Engage Your Customers and Drive Growth
-


How Chief Product Officers Drive Revenue Acceleration
-


Digital transformation as a service is poised to drive enterprise growth
-


Infosys and SAP together drive business innovation for clients
Tech
The hunter-gatherer groups at the heart of a microbiome gold rush
Published
4 months agoon
12/19/2023By
Drew Simpson
The first step to finding out is to catalogue what microbes we might have lost. To get as close to ancient microbiomes as possible, microbiologists have begun studying multiple Indigenous groups. Two have received the most attention: the Yanomami of the Amazon rainforest and the Hadza, in northern Tanzania.
Researchers have made some startling discoveries already. A study by Sonnenburg and his colleagues, published in July, found that the gut microbiomes of the Hadza appear to include bugs that aren’t seen elsewhere—around 20% of the microbe genomes identified had not been recorded in a global catalogue of over 200,000 such genomes. The researchers found 8.4 million protein families in the guts of the 167 Hadza people they studied. Over half of them had not previously been identified in the human gut.
Plenty of other studies published in the last decade or so have helped build a picture of how the diets and lifestyles of hunter-gatherer societies influence the microbiome, and scientists have speculated on what this means for those living in more industrialized societies. But these revelations have come at a price.
A changing way of life
The Hadza people hunt wild animals and forage for fruit and honey. “We still live the ancient way of life, with arrows and old knives,” says Mangola, who works with the Olanakwe Community Fund to support education and economic projects for the Hadza. Hunters seek out food in the bush, which might include baboons, vervet monkeys, guinea fowl, kudu, porcupines, or dik-dik. Gatherers collect fruits, vegetables, and honey.
Mangola, who has met with multiple scientists over the years and participated in many research projects, has witnessed firsthand the impact of such research on his community. Much of it has been positive. But not all researchers act thoughtfully and ethically, he says, and some have exploited or harmed the community.
One enduring problem, says Mangola, is that scientists have tended to come and study the Hadza without properly explaining their research or their results. They arrive from Europe or the US, accompanied by guides, and collect feces, blood, hair, and other biological samples. Often, the people giving up these samples don’t know what they will be used for, says Mangola. Scientists get their results and publish them without returning to share them. “You tell the world [what you’ve discovered]—why can’t you come back to Tanzania to tell the Hadza?” asks Mangola. “It would bring meaning and excitement to the community,” he says.
Some scientists have talked about the Hadza as if they were living fossils, says Alyssa Crittenden, a nutritional anthropologist and biologist at the University of Nevada in Las Vegas, who has been studying and working with the Hadza for the last two decades.
The Hadza have been described as being “locked in time,” she adds, but characterizations like that don’t reflect reality. She has made many trips to Tanzania and seen for herself how life has changed. Tourists flock to the region. Roads have been built. Charities have helped the Hadza secure land rights. Mangola went abroad for his education: he has a law degree and a master’s from the Indigenous Peoples Law and Policy program at the University of Arizona.
Tech
The Download: a microbiome gold rush, and Eric Schmidt’s election misinformation plan
Published
4 months agoon
12/18/2023By
Drew Simpson
Over the last couple of decades, scientists have come to realize just how important the microbes that crawl all over us are to our health. But some believe our microbiomes are in crisis—casualties of an increasingly sanitized way of life. Disturbances in the collections of microbes we host have been associated with a whole host of diseases, ranging from arthritis to Alzheimer’s.
Some might not be completely gone, though. Scientists believe many might still be hiding inside the intestines of people who don’t live in the polluted, processed environment that most of the rest of us share. They’ve been studying the feces of people like the Yanomami, an Indigenous group in the Amazon, who appear to still have some of the microbes that other people have lost.
But there is a major catch: we don’t know whether those in hunter-gatherer societies really do have “healthier” microbiomes—and if they do, whether the benefits could be shared with others. At the same time, members of the communities being studied are concerned about the risk of what’s called biopiracy—taking natural resources from poorer countries for the benefit of wealthier ones. Read the full story.
—Jessica Hamzelou
Eric Schmidt has a 6-point plan for fighting election misinformation
—by Eric Schmidt, formerly the CEO of Google, and current cofounder of philanthropic initiative Schmidt Futures
The coming year will be one of seismic political shifts. Over 4 billion people will head to the polls in countries including the United States, Taiwan, India, and Indonesia, making 2024 the biggest election year in history.
Tech
Navigating a shifting customer-engagement landscape with generative AI
Published
4 months agoon
12/18/2023By
Drew Simpson
A strategic imperative
Generative AI’s ability to harness customer data in a highly sophisticated manner means enterprises are accelerating plans to invest in and leverage the technology’s capabilities. In a study titled “The Future of Enterprise Data & AI,” Corinium Intelligence and WNS Triange surveyed 100 global C-suite leaders and decision-makers specializing in AI, analytics, and data. Seventy-six percent of the respondents said that their organizations are already using or planning to use generative AI.
According to McKinsey, while generative AI will affect most business functions, “four of them will likely account for 75% of the total annual value it can deliver.” Among these are marketing and sales and customer operations. Yet, despite the technology’s benefits, many leaders are unsure about the right approach to take and mindful of the risks associated with large investments.
Mapping out a generative AI pathway
One of the first challenges organizations need to overcome is senior leadership alignment. “You need the necessary strategy; you need the ability to have the necessary buy-in of people,” says Ayer. “You need to make sure that you’ve got the right use case and business case for each one of them.” In other words, a clearly defined roadmap and precise business objectives are as crucial as understanding whether a process is amenable to the use of generative AI.
The implementation of a generative AI strategy can take time. According to Ayer, business leaders should maintain a realistic perspective on the duration required for formulating a strategy, conduct necessary training across various teams and functions, and identify the areas of value addition. And for any generative AI deployment to work seamlessly, the right data ecosystems must be in place.
Ayer cites WNS Triange’s collaboration with an insurer to create a claims process by leveraging generative AI. Thanks to the new technology, the insurer can immediately assess the severity of a vehicle’s damage from an accident and make a claims recommendation based on the unstructured data provided by the client. “Because this can be immediately assessed by a surveyor and they can reach a recommendation quickly, this instantly improves the insurer’s ability to satisfy their policyholders and reduce the claims processing time,” Ayer explains.
All that, however, would not be possible without data on past claims history, repair costs, transaction data, and other necessary data sets to extract clear value from generative AI analysis. “Be very clear about data sufficiency. Don’t jump into a program where eventually you realize you don’t have the necessary data,” Ayer says.
The benefits of third-party experience
Enterprises are increasingly aware that they must embrace generative AI, but knowing where to begin is another thing. “You start off wanting to make sure you don’t repeat mistakes other people have made,” says Ayer. An external provider can help organizations avoid those mistakes and leverage best practices and frameworks for testing and defining explainability and benchmarks for return on investment (ROI).
Using pre-built solutions by external partners can expedite time to market and increase a generative AI program’s value. These solutions can harness pre-built industry-specific generative AI platforms to accelerate deployment. “Generative AI programs can be extremely complicated,” Ayer points out. “There are a lot of infrastructure requirements, touch points with customers, and internal regulations. Organizations will also have to consider using pre-built solutions to accelerate speed to value. Third-party service providers bring the expertise of having an integrated approach to all these elements.”
