Politics
In-House Counsel Team: The Profound Influence of Generative AI
Published
9 months agoon
By
Drew Simpson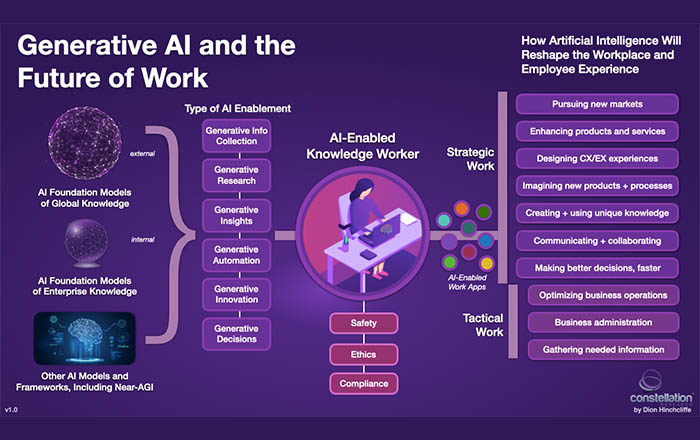
In the present digital world, technology is transforming all sectors. So too, is it making deep inroads into the legal world, enhancing and expediting both routine and complex tasks undertaken by in-house counsel teams.
This blog focuses on a particular computing invention known as “Generative AI,” a relatively new artificial intelligence technology that empowers businesses to undertake tedious processes quickly and more accurately aided by machines rather than lawyers.
We explore how generative AI can unlock added potential for in-house counsel teams while illuminating any possible challenges or ethical considerations attached to it. By contemplating the advantages of this technology as well as the implications of integrating it into practice law processes, we are better equipped to take advantage of available technologies without compromising human values.
Understanding Generative AI
Generative AI is a software technology that creates data and content in a fashion that can teach the system more with each generation. Rather than telling it precisely what to do, generators provide general parameters allowing them to learn independently by exploring an unrestricted range of possible solutions.
Generative AI employs self-teaching algorithms and uses deep learning techniques. It can be used for tasks, such as image processing, natural language processing, drug discovery simulation, mathematical optimization, and several other problem-solving applications.
Alongside its ever-growing process automation capabilities, generative AI has become increasingly important in fields ranging from logistics and finance to healthcare and cybersecurity.
Applications of generative AI in various industries, including law
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence technology capable of generating new content autonomously. It can learn from existing material and create brand-new data adapted to meet specific criteria.
In the legal industry, this form of AI enables faster research, document drafting, contract analysis, and other activities normally handled by human lawyers. Generative AI programs are used for automated legal document generation, jurisdiction-specific document review, and intelligent suggestions when negotiating contracts.
The potential applications of generative AI in the law range from knowledge graphing to understanding nuanced user queries.
It’s being utilized in many countries with success. Diverse industries such as banking and finance can all take advantage of generative AI’s superior predictive capabilities.
How generative AI differs from traditional AI tools
Generative AI is a form of Artificial Intelligence that can generate unique results such as text, images, or sound from code.
Unlike traditional AI tools like machine learning and deep learning, which are used primarily to solve one set problem, generative AI can “think” outside of the box when creating original work by predicting what will likely happen given a certain set of inputs.
It goes beyond merely aiding decision-making within predefined rules; its capabilities allow it to make novel insights. Furthermore, unlike deep learning models that need pre-labeled data for accuracy and correctness, generative AI solutions use unstructured data sets, leading to more accurate predictions due to their lack of constraints on available information pathways.
Advantages of Integrating Generative AI in Legal Practice

Enhanced legal research capabilities
Generative AI offers a range of advantages for legal practitioners in their day-to-day operations. One of the key benefits is its enhanced capability for conducting legal research tasks.
Generative AI leverages natural language processing tools to literally interpret and summarize multiple documents containing legal expertise within seconds, replacing laborious manual processes which take days.
It gives lawyers access to real-time data from structured (courthouse records) and unstructured (published cases) sources, allowing them to quickly and accurately organize it into useful information quickly and accurately.
This provides insights on current developments in legal issues and potential pivotal points for decision-making that would traditionally take many hours or days to collate manually.
Time and cost-efficiency in drafting legal documents
Integrating generative AI technology into legal practices can help to improve time and cost efficiency in drafting legal documents.
Generative modeling technologies can quickly read contract clauses, distill them into their components, interpret the relationships between those elements, and ultimately use that knowledge to generate customized, legally compliant documents based on user needs.
This automates much of the contract writing process and leads to fewer errors or audits and shorter reviews/approval times — all while saving considerable money spent on manual labor. Drafting agreements using generative AI thus significantly improves the productivity of both an organization’s human resources and financial capital.
Improved contract analysis and management
Improved contract analysis and management is one of the significant advantages of integrating generative AI in legal practice.
Generative AI tools employ Natural Language™ processing, or NLP, capable of extracting meaning from a vast range of contracts. Through AI-powered analytics, lawyers can access concisely summarized key information like likely outcomes or relevant obligations with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
Updated search mechanisms enable users to rapidly track down critical points reached across all stages during negotiations. Additionally, automation also helps eliminate administrative costs and trivial, time-consuming tasks that often distract the proper execution of strategic decisions by in-house counsel teams.
Mitigation of human error and bias in legal tasks
Generative AI offers the legal sector a valuable tool to reduce human error and bias when making and executing decisions. Generative AI automates ancient decision models by providing more comprehensive analysis powered by machine learning algorithms that can detect patterns in data sets without any prior programming.
This reduces the time it takes for legal professionals to stay updated on regulations as they change or across global jurisdictions.
Generative AI also assists in detecting previously overlooked discrepancies in the language used throughout documents which would have gone unnoticed if worked on manually. In addition, policy compliance becomes faster and more accurate as errors are quickly identified before any damaging outcomes arise.
Therefore, the implementation of generative AI helps standardize input calculation while increasing efficiency and cost-effectiveness within legal work.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations

Potential risks associated with using generative AI in the legal sector
When introducing generative AI into the legal sector, organizations must ascertain that potential risks are mitigated, and appropriate consideration for various ethical implications arising from automation is prioritized.
The main challenges associated with using generative AI in the context of legal practice arise from its reliance on past big data which may contain inherent biases; moreover, any errors or unintended issues in generated outputs can carry both commercial and reputational impacts.
Also key to its successful adoption is reinforcing compliance regulations concerning usage, storage, and accessibility patterns when organizational staff deploy automated tools for conducting lawyers’ tasks.
Ensuring data privacy and confidentiality
The release of data generated by generative AI technologies in legal practice can be vulnerable to infringement, unauthorized access, and misuse by untrustworthy actors.
Data creators should be given full control over how their protected information is handled during AI processing; they must also have a certain degree of trust in the organization handling their sensitive data.
To ensure data privacy and confidentiality in accordance with applicable laws or data protection regulations, organizations should strive to create well-implemented security solutions that depend on legitimate client identifications as protective measures against unauthorized personnel.
Organizations should also secure intelligently generated textual documents for better all-around safety when organizing economic endeavors.
Addressing ethical concerns related to AI-generated content
Addressing ethical concerns related to AI-generated content is essential in integrating generative AI into legal practice.
Investigating the products’ algorithmic biases and implementation strategies are key practices while reducing any scope for optimization from problematic data sources should be observed.
Further issues can arise, such as fairness to citizens/consumers — questions we hope can be tackled by democratic debates between lawyers, decision-makers, technologists, ad scholars within this realm of development ethics surrounding artificial intelligence.
Impact on In-House Counsel Teams
Streamlined workflow and increased productivity
Integrating generative AI technology into in-house counsel teams enhances their productivity by utilizing AI capabilities to automate and streamline legal hurdles.
By expediting mundane tasks like processing data sets and contract analysis/analytics, which involve cognition-related activities, in-house lawyers have more time for problem-solving associated with more complicated contracts.
In-house teams can then add significantly broader value to businesses compared to before.
Empowerment of legal professionals to focus on higher-value tasks
Integrating generative AI technology with in-house counsel teams enables legal professionals to focus on the more valuable aspects of their job.
By relying on AI tools for daily operations such as analytic research, preliminary forms, and regulations assessments, drafted documents can be completed faster and with less effort.
This makes it possible for in-house counsels to spend their time working on tougher and higher value tasks such as structuring and reorganizing complex contracts or eliminating existing conflicts—valuable results than before could not be reached by old law modeling executions alone.
Transforming the role of in-house counsel in organizations
The role of in-house counsel is rapidly being transformed by adopting generative AI technology.
By leveraging state-of-art AI to automate tedious, administrative tasks, generative AI enables in-house counsel teams to focus on higher-value tasks such as developing novel legal strategies or devising high-impact campaigns.
Automation also helps team members adapt and think critically—freeing up resources and empowering them with decision-making power over higher-impact initiatives.
Generative AI furthermore shifts commercial law away from traditional staffing models towards interdisciplinary approaches involving technically advanced guidance and improved performance of the corporate legal function.
Successful Integration of Generative AI
Identifying suitable use cases for generative AI within the team
Integrating generative AI successfully into in-house counsel teams starts by identifying useful and realistic use cases that give value to daily tasks. Issues such as compliance reviews, contract negotiation tracking systems, and research analysis can benefit from the application of dynamically generated text.
By assessing the law firm’s frequently queries areas, potential use cases for the technology may be identified corresponding to current workflows and processes similarly evaluated.
Leveraging human knowledge and machine refinement further streamlines rules efficiently in various stages or steps of decision-making across legal operations teams.
Selecting the right generative AI tools and platforms
Selecting the right generative AI tools and platforms to integrate into existing legal operations is key for successfully implementing such technology.
Generally speaking, organizations should consider user-friendly solutions which will not require excessive training.
It is also vital for firms to conduct demos with multiple teams and assess different vendors to identify the ones that present suitable features capable of satisfying their needs in terms of cost benefits analysis, timeline assessment, and ease of use.
Furthermore, security, data management capabilities, and scalability must be systematically considered.
Training and upskilling in-house counsel to adapt to AI integration
Considering the broad range of functions available to machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence technologies, upskilling in-house counsel can be crucial for successfully integrating generative AI. Legal professionals must be adequately prepared to utilize AI tools while understanding their practical applications.
Effective training methods such as e-learning modules, webcasts, mock trials, and laboratories can equip lawyers with important technical knowledge about implementing automated tasks professionally.
In addition to foundational learnings about current standards on privacy protection and ethical implications, this technical competency also enhances problem-solving capacity by sharpening human cognitive skills that are extraneous from elemental computation skill requirements.
Collaboration between legal experts and AI technology specialists
For generative AI to be successfully integrated into the legal sector, meaningful collaboration must occur between law professionals and AI technology specialists.
Lawyers should solicit technical advice in determining ideal use cases for generative AI while technology experts can lend expertise regarding the selection of appropriate tools and platforms for implementation.
Further, lawyers and tech specialists work together to train end users to make optimal use of the platform. With a qualified team behind them, in-house counsel stands to benefit significantly from adapting well-tailored solutions catalyzed by generative AI into their workflows & increase productivity as a result.
Conclusion
In conclusion, integrating generative AI brings numerous challenges and ethical considerations that legal professionals have to grapple with.
However, if implemented correctly, this technology promises powerful advantages for in-house counsel teams, including enhanced legal research capabilities, increased productivity, and improved contract analysis.
Generative AI can no doubt revolutionize how everyday law is practiced, thereby evolving the role of in-house counsel in organizations.
Ultimately legal professionals must remain apprised of new technological trends while being cognizant of protecting data privacy and upholding ethical standards. By proactively harnessing these tools responsibly, we can power the next-gen approach to legal services.
Featured Image Credit: Photo by August de Richelieu; Pexels; Thank you!
Timothy Carter
Chief Revenue Officer
Timothy Carter is the Chief Revenue Officer of the Seattle digital marketing agency SEO.co, DEV.co & Law.co. He has spent more than 20 years in the world of SEO and digital marketing leading, building and scaling sales operations, helping companies increase revenue efficiency and drive growth from websites and sales teams. When he’s not working, Tim enjoys playing a few rounds of disc golf, running, and spending time with his wife and family on the beach — preferably in Hawaii with a cup of Kona coffee. Follow him on Twitter @TimothyCarter
You may like
-


Navigating a shifting customer-engagement landscape with generative AI
-

Now we know what OpenAI’s superalignment team has been up to
-


Making an image with generative AI uses as much energy as charging your phone
-
Finding value in generative AI for financial services
-


The Download: what is death, and jailbreaking generative AI
-

Humans at the heart of generative AI
Politics
Fintech Kennek raises $12.5M seed round to digitize lending
Published
7 months agoon
10/11/2023By
Drew Simpson
London-based fintech startup Kennek has raised $12.5 million in seed funding to expand its lending operating system.
According to an Oct. 10 tech.eu report, the round was led by HV Capital and included participation from Dutch Founders Fund, AlbionVC, FFVC, Plug & Play Ventures, and Syndicate One. Kennek offers software-as-a-service tools to help non-bank lenders streamline their operations using open banking, open finance, and payments.
The platform aims to automate time-consuming manual tasks and consolidate fragmented data to simplify lending. Xavier De Pauw, founder of Kennek said:
“Until kennek, lenders had to devote countless hours to menial operational tasks and deal with jumbled and hard-coded data – which makes every other part of lending a headache. As former lenders ourselves, we lived and breathed these frustrations, and built kennek to make them a thing of the past.”
The company said the latest funding round was oversubscribed and closed quickly despite the challenging fundraising environment. The new capital will be used to expand Kennek’s engineering team and strengthen its market position in the UK while exploring expansion into other European markets. Barbod Namini, Partner at lead investor HV Capital, commented on the investment:
“Kennek has developed an ambitious and genuinely unique proposition which we think can be the foundation of the entire alternative lending space. […] It is a complicated market and a solution that brings together all information and stakeholders onto a single platform is highly compelling for both lenders & the ecosystem as a whole.”
The fintech lending space has grown rapidly in recent years, but many lenders still rely on legacy systems and manual processes that limit efficiency and scalability. Kennek aims to leverage open banking and data integration to provide lenders with a more streamlined, automated lending experience.
The seed funding will allow the London-based startup to continue developing its platform and expanding its team to meet demand from non-bank lenders looking to digitize operations. Kennek’s focus on the UK and Europe also comes amid rising adoption of open banking and open finance in the regions.
Featured Image Credit: Photo from Kennek.io; Thank you!
Radek Zielinski
Radek Zielinski is an experienced technology and financial journalist with a passion for cybersecurity and futurology.
Politics
Fortune 500’s race for generative AI breakthroughs
Published
7 months agoon
10/11/2023By
Drew Simpson
As excitement around generative AI grows, Fortune 500 companies, including Goldman Sachs, are carefully examining the possible applications of this technology. A recent survey of U.S. executives indicated that 60% believe generative AI will substantially impact their businesses in the long term. However, they anticipate a one to two-year timeframe before implementing their initial solutions. This optimism stems from the potential of generative AI to revolutionize various aspects of businesses, from enhancing customer experiences to optimizing internal processes. In the short term, companies will likely focus on pilot projects and experimentation, gradually integrating generative AI into their operations as they witness its positive influence on efficiency and profitability.
Goldman Sachs’ Cautious Approach to Implementing Generative AI
In a recent interview, Goldman Sachs CIO Marco Argenti revealed that the firm has not yet implemented any generative AI use cases. Instead, the company focuses on experimentation and setting high standards before adopting the technology. Argenti recognized the desire for outcomes in areas like developer and operational efficiency but emphasized ensuring precision before putting experimental AI use cases into production.
According to Argenti, striking the right balance between driving innovation and maintaining accuracy is crucial for successfully integrating generative AI within the firm. Goldman Sachs intends to continue exploring this emerging technology’s potential benefits and applications while diligently assessing risks to ensure it meets the company’s stringent quality standards.
One possible application for Goldman Sachs is in software development, where the company has observed a 20-40% productivity increase during its trials. The goal is for 1,000 developers to utilize generative AI tools by year’s end. However, Argenti emphasized that a well-defined expectation of return on investment is necessary before fully integrating generative AI into production.
To achieve this, the company plans to implement a systematic and strategic approach to adopting generative AI, ensuring that it complements and enhances the skills of its developers. Additionally, Goldman Sachs intends to evaluate the long-term impact of generative AI on their software development processes and the overall quality of the applications being developed.
Goldman Sachs’ approach to AI implementation goes beyond merely executing models. The firm has created a platform encompassing technical, legal, and compliance assessments to filter out improper content and keep track of all interactions. This comprehensive system ensures seamless integration of artificial intelligence in operations while adhering to regulatory standards and maintaining client confidentiality. Moreover, the platform continuously improves and adapts its algorithms, allowing Goldman Sachs to stay at the forefront of technology and offer its clients the most efficient and secure services.
Featured Image Credit: Photo by Google DeepMind; Pexels; Thank you!
Deanna Ritchie
Managing Editor at ReadWrite
Deanna is the Managing Editor at ReadWrite. Previously she worked as the Editor in Chief for Startup Grind and has over 20+ years of experience in content management and content development.
Politics
UK seizes web3 opportunity simplifying crypto regulations
Published
7 months agoon
10/10/2023By
Drew Simpson
As Web3 companies increasingly consider leaving the United States due to regulatory ambiguity, the United Kingdom must simplify its cryptocurrency regulations to attract these businesses. The conservative think tank Policy Exchange recently released a report detailing ten suggestions for improving Web3 regulation in the country. Among the recommendations are reducing liability for token holders in decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) and encouraging the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) to adopt alternative Know Your Customer (KYC) methodologies, such as digital identities and blockchain analytics tools. These suggestions aim to position the UK as a hub for Web3 innovation and attract blockchain-based businesses looking for a more conducive regulatory environment.
Streamlining Cryptocurrency Regulations for Innovation
To make it easier for emerging Web3 companies to navigate existing legal frameworks and contribute to the UK’s digital economy growth, the government must streamline cryptocurrency regulations and adopt forward-looking approaches. By making the regulatory landscape clear and straightforward, the UK can create an environment that fosters innovation, growth, and competitiveness in the global fintech industry.
The Policy Exchange report also recommends not weakening self-hosted wallets or treating proof-of-stake (PoS) services as financial services. This approach aims to protect the fundamental principles of decentralization and user autonomy while strongly emphasizing security and regulatory compliance. By doing so, the UK can nurture an environment that encourages innovation and the continued growth of blockchain technology.
Despite recent strict measures by UK authorities, such as His Majesty’s Treasury and the FCA, toward the digital assets sector, the proposed changes in the Policy Exchange report strive to make the UK a more attractive location for Web3 enterprises. By adopting these suggestions, the UK can demonstrate its commitment to fostering innovation in the rapidly evolving blockchain and cryptocurrency industries while ensuring a robust and transparent regulatory environment.
The ongoing uncertainty surrounding cryptocurrency regulations in various countries has prompted Web3 companies to explore alternative jurisdictions with more precise legal frameworks. As the United States grapples with regulatory ambiguity, the United Kingdom can position itself as a hub for Web3 innovation by simplifying and streamlining its cryptocurrency regulations.
Featured Image Credit: Photo by Jonathan Borba; Pexels; Thank you!
Deanna Ritchie
Managing Editor at ReadWrite
Deanna is the Managing Editor at ReadWrite. Previously she worked as the Editor in Chief for Startup Grind and has over 20+ years of experience in content management and content development.
